Thinking about the keto diet to manage diabetes? It's a low-carb, high-fat eating plan designed to help control blood sugar levels. By slashing carbs to 20-50 grams a day, your body switches to burning fat for fuel – pretty cool, right? This can lead to better insulin sensitivity and more stable blood sugar levels. But wait, don't forget to keep an eye on your blood sugar and chat with your doctor first. You might also experience 'keto flu' at the start, but many find the benefits worth it. Curious about the ins and outs of this approach? There's more to uncover.
Key Takeaways
- The ketogenic diet helps manage diabetes by significantly improving insulin sensitivity and reducing HbA1c levels.
- Limiting carbohydrate intake to 20-50 grams daily promotes ketosis, which stabilizes blood sugar levels.
- Regular blood sugar and ketone monitoring are essential for effective diabetes management on the keto diet.
- Keto diets offer significant short-term improvements in blood glucose control compared to other diets.
- Potential risks include hypoglycemia and nutrient deficiencies, necessitating medical supervision during the diet.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as keto, involves a stringent reduction of carbohydrate intake to approximately 20-50 grams per day, propelling the body into a metabolic state known as ketosis. This state means your body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
Keto basics are pretty straightforward: you eat mostly fats, a moderate amount of protein, and very few carbs. Imagine your plate filled with avocado, cheese, and meat, but not much bread or pasta.
Carb reduction is the key to this diet. By cutting down on carbs, your body switches to burning fat for fuel, which can help with weight loss and maintaining steady energy levels. Originally, keto was developed to help kids with epilepsy, but now it's being looked at for other benefits too.
On a typical keto diet, about 70% of your daily calories come from fat, 20% from protein, and only 10% from carbs. It's like a food adventure, exploring new recipes and foods you might not have tried before.
But remember, before starting any diet, especially one like keto, it's important to talk to a healthcare professional to make sure it's safe for you.
Benefits for Type 2 Diabetes
Many individuals with type 2 diabetes can experience considerable improvements in their condition by adopting a ketogenic diet. This low-carb, high-fat diet can bring about numerous health benefits that are particularly advantageous for managing type 2 diabetes.
One of the primary benefits is weight loss. Research shows that participants on a ketogenic diet can experience an average weight loss of around 8%. This reduction in body weight can greatly enhance insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to manage blood sugar levels.
Moreover, the ketogenic diet has been shown to lead to notable reductions in HbA1c levels, a vital marker for long-term blood sugar management. Improved HbA1c levels indicate better overall glycemic control, which is essential for diabetes management.
Additional benefits include:
- Participants often report more stable blood sugar levels with fewer fluctuations, reducing the risk of hyperglycemic episodes.
- The ketogenic diet can lower triglyceride levels and increase HDL cholesterol, which are both beneficial for heart health in diabetics.
- Many individuals following this diet may reduce their reliance on anti-diabetic medications for up to 12 months due to improved blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Effective blood sugar monitoring is essential for individuals on a ketogenic diet, particularly during the initial adjustment phase. This is because as your body adapts to lower carbs, keeping an eye on blood glucose levels helps you stay safe and avoid hypoglycemia. Regular blood glucose testing should be personalized to your health needs. You might need to tweak your insulin or diabetes medications as your carbohydrate intake drops.
But don't stop at blood glucose! Ketone monitoring is equally important. Ketones show if your body is in ketosis, the fat-burning state you want. Ideal ketone levels are usually between 1.5 to 3.0 mmol/L. If you notice any signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) like high blood sugar, nausea, or fruity breath, seek medical help right away.
Using continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can make this easier. They provide real-time feedback on your blood sugar levels, helping you make smarter dietary choices.
Monitoring doesn't have to be a chore. Think of it as your way of keeping tabs on how well your body adapts to the keto lifestyle. Stay proactive, and you'll master this adjustment smoothly!
Scientific Evidence
Scientific research shows that the keto diet can have big benefits for people with type 2 diabetes, especially in controlling blood sugar levels.
Studies have found that this diet helps people lose weight and greatly lower their blood glucose levels in just 12 weeks.
However, while the short-term results are impressive, more research is needed to understand how well it works in the long run compared to other diets like the Mediterranean diet.
Proven Health Benefits
Through rigorous scientific investigation, the ketogenic diet has demonstrated important health benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Embracing a keto lifestyle, which emphasizes nutritional balance, has led to remarkable outcomes for many. For instance, the keto diet has shown to reduce HbA1c levels considerably, marking long-term blood sugar control. This is fantastic news for those managing diabetes!
Moreover, studies reveal that participants following this diet experienced an average weight loss of 8%, alongside a decrease in insulin requirements. This dual benefit not only aids in weight management but also reduces dependency on medication, a win-win situation.
Another key finding is the notable improvement in insulin sensitivity seen in individuals on a ketogenic diet compared to those on a standard diet. This means that the body becomes more efficient at using insulin, which is essential for managing diabetes.
- The ketogenic diet led to a 9% reduction in blood glucose levels.
- Evidence suggests lower triglyceride levels and increased HDL cholesterol.
- Improved long-term blood sugar control with reduced HbA1c levels.
Glycemic Control Studies
Amid growing interest in dietary interventions for diabetes management, systematic reviews have highlighted the ketogenic diet's potential to considerably lower HbA1c levels, thereby indicating enhanced long-term blood sugar control for individuals with type 2 diabetes. This diet isn't just a fad—it's showing real promise!
A 2022 review found the keto diet can provide short-term benefits for glycemic control and a striking 9% drop in blood glucose levels. That's quite impressive when you reflect on it.
What makes the ketogenic diet so effective? A big part of it is keto adaptation, where your body adjusts to burning fats instead of carbs. This switch can help improve insulin response, making it easier to manage blood sugar levels.
And here's another kicker: studies show that weight loss associated with the keto diet can further boost insulin sensitivity. It's like hitting two birds with one stone!
Moreover, research indicates that people on the keto diet might need less medication for diabetes. Some have even seen reduced dependency on meds for up to 12 months! This diet could be a game-changer for those struggling to manage their diabetes.
Comparative Diet Research
Recent comparative studies have provided valuable insights into the effectiveness of the ketogenic diet versus the Mediterranean diet for diabetes management. Conducted between June 2019 and December 2020, the study involved 40 adults and revealed fascinating results. Both diets led to similar improvements in blood glucose control, with a 9% drop on the ketogenic diet and a 7% drop on the Mediterranean diet. Weight loss was also comparable, with participants losing an average of 8% of their body weight on the ketogenic diet and 7% on the Mediterranean diet.
However, there were some important differences:
- LDL cholesterol levels increased on the ketogenic diet while they decreased on the Mediterranean diet.
- Some participants found the ketogenic diet too restrictive, which affected their long-term adherence.
- Post-trial evaluations showed a preference for the Mediterranean diet among participants for long-term sustainability.
These findings suggest that dietary preferences and lifestyle choices play significant roles in the effectiveness and sustainability of these diets.
While both limit added sugars and refined grains, the Mediterranean diet seemed more manageable for long-term adherence, possibly making it a better option for some individuals. This highlights the importance of choosing a diet that aligns well with one's lifestyle and preferences.
Keto Meal Planning
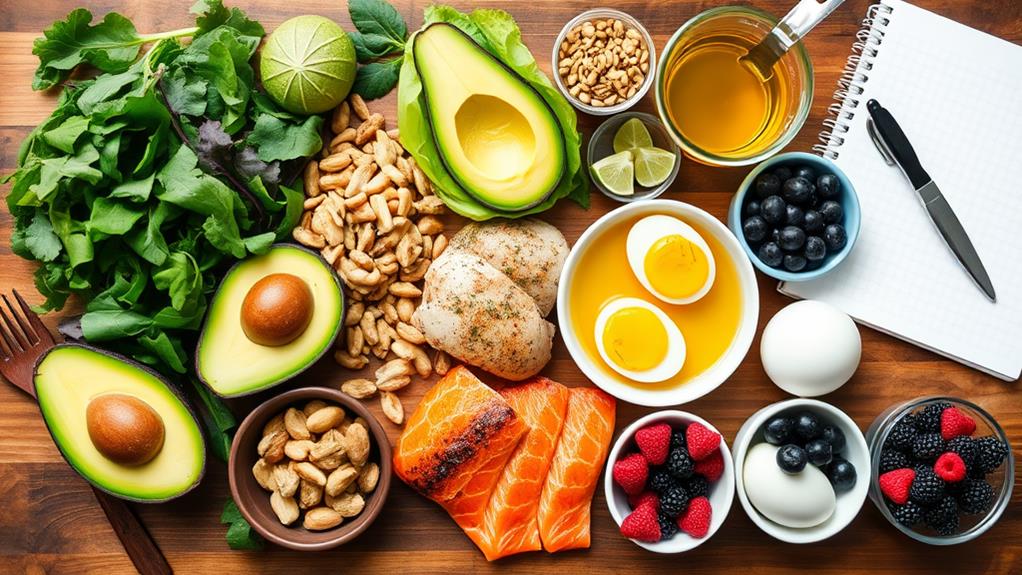

Effective keto meal planning is vital for diabetics aiming to manage their condition through dietary means. To begin, selecting keto recipe ideas that balance macronutrients is essential. Typically, the goal is 70% fat, 20% protein, and 10% carbohydrates, with daily carbs limited to 20-50 grams to maintain ketosis.
Incorporate a variety of low-carb foods like leafy greens, avocados, eggs, fish, nuts, and healthy fats such as olive oil. Avoid high-carb foods like grains, sugars, and starchy vegetables.
Meal prep tips can be a lifesaver. Preparing meals in advance helps you stick to the keto diet, reducing dependence on convenience foods that often hide carbs. Keeping a food diary or using a tracking app can help monitor your macronutrient intake and guarantee you stay within your carb limits. This proactive approach can make a world of difference.
Additionally, regularly checking your blood glucose levels, especially when starting, helps you see how different foods affect your body. This way, you can make necessary adjustments to your diet. Tailoring your meal plan through careful monitoring and preparation guarantees better blood sugar management and a smoother keto journey.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
The ketogenic diet, while beneficial for many diabetics, carries several potential risks and side effects that should be carefully considered. One of the most commonly reported short-term side effects is the "keto flu," which can cause symptoms like fatigue, headache, nausea, and digestive issues. These symptoms typically last from a few days to weeks as the body adjusts to ketosis.
In addition to the keto flu, there are long-term risks to be aware of, such as nutrient deficiencies. The limited variety of foods allowed on a ketogenic diet can lead to a lack of essential vitamins and minerals.
Furthermore, individuals with type 1 diabetes or uncontrolled type 2 diabetes are at risk for ketoacidosis, a serious condition marked by extremely high blood ketone levels. Although rare in type 2 diabetes, it is vital to monitor for this condition.
Other potential risks include:
- Hypoglycemia: Significant reductions in blood sugar levels can occur, especially if you are taking insulin or other diabetes medications.
- Kidney stones and dyslipidemia: These conditions may develop over time due to the diet's high fat content.
- Fatty liver disease: A long-term risk associated with the ketogenic diet.
Continuous monitoring of blood glucose is essential to safely adjust medication dosages and prevent adverse health effects.
Long-Term Sustainability

Adhering to the ketogenic diet over the long term can be particularly challenging due to its restrictive nature. Many people find it hard to stick with compared to more balanced diets like the Mediterranean diet. The keto diet's strict limits on carbs mean less dietary flexibility, which can make meal prep a real chore. Let's face it, who wants to think about carbs every time they eat?
Studies show that while keto can help control blood sugar in the short term, it doesn't offer extra long-term health benefits compared to diets with more variety. When participants switched from meal delivery to making their own meals, their adherence scores dropped. This highlights how significant convenience and meal prep are for sticking with the diet.
Reducing added sugars and refined grains is key for managing diabetes. Sustainable eating habits are essential for long-term health. Personalized diets that balance carbs with nutrient-rich foods can support blood sugar control and overall health.
Here's a quick comparison to help you out:
| Aspect | Keto Diet | Balanced Diets (e.g., Mediterranean) |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Flexibility | Low | High |
| Meal Prep | Time-consuming | Moderate |
| Short-term Benefits | High | Moderate |
| Long-term Benefits | Moderate | High |
| Adherence Scores | Decrease with self-prep meals | More stable |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Keto and Low-Carb Good for Diabetics?
The keto benefits for diabetics include improved blood sugar control and reduced HbA1c levels. However, low carb challenges, such as potential hypoglycemia, necessitate close monitoring and personalized dietary adjustments to guarantee safety and effectiveness.
Can You Have Low Blood Sugar on Keto Diet?
Yes, individuals can experience low blood sugar on a keto diet, particularly during keto adaptation. Blood sugar fluctuations may occur, necessitating careful monitoring and potential medication adjustments to prevent hypoglycemia, especially in diabetic patients.
Does Cutting Down on Carbs Help With Diabetes?
Yes, cutting down on carbs can help with diabetes. Carb reduction can greatly improve blood sugar control, leading to lower HbA1c levels, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and decreased fluctuations in blood glucose, thereby promoting better diabetes management.
Why Is It Bad for Diabetics to Go Into Ketosis?
Entering ketosis can exacerbate diabetic symptoms, including the risk of ketoacidosis, which leads to severe metabolic disturbances. Additionally, ketosis effects can cause blood sugar fluctuations, complicating diabetes management and potentially resulting in hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ketogenic diet offers potential benefits for managing Type 2 diabetes, including improved blood sugar control and weight loss. It is vital to monitor blood sugar levels regularly and consult healthcare professionals before starting this diet. While scientific evidence supports its benefits, potential risks and side effects must be considered. Thoughtful keto meal planning and awareness of long-term sustainability are essential for safe and effective diabetes management through a low-carb approach.









No Comments