
Monitoring ketone levels is essential on a keto diet. To accurately check ketones, use blood testing for the most precise results. Aim for levels between 0.5-3.0 mmol/L for nutritional ketosis. Urine strips are affordable but less reliable over time, while breath tests offer non-invasive options. Test consistently at the same time daily, ideally in a fasting state. Hydration and proper insulin management prevent high ketone buildup. Recognize symptoms like fruity breath and fatigue as indicators of increased ketones. Using an established routine and tracking trends helps maintain desired ketosis. Continue for an all-encompassing understanding of effective ketone monitoring.
Key Takeaways
- Consistent Timing: Test ketone levels at the same time each day, ideally in a fasting state, for consistent and reliable results.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated to prevent dehydration and help maintain accurate ketone readings.
- Testing Method: Use blood ketone meters for the most precise measurements, especially during the initial stages of the diet.
- Symptom Awareness: Be aware of symptoms like fruity breath, fatigue, and increased thirst, which can indicate elevated ketone levels.
- Log Results: Maintain a log of ketone levels, dietary intake, and physical activity to track trends and identify patterns.
Understand Ketones
Ketones are biochemical compounds produced by the liver during periods of low carbohydrate intake, serving as an alternative energy source to glucose. This process, known as ketone production, occurs when the body metabolizes fats due to insufficient carbohydrate availability.
The resultant metabolic state, termed ketosis, is characterized by the presence of ketones in the blood, urine, or breath. Monitoring ketone levels is vital for confirming ketosis status, guaranteeing that one remains within the physiological range for nutritional ketosis, typically between 0.5 to 3.0 mmol/L.
This range is significant for reaping ketosis benefits such as weight loss and enhanced mental clarity. These benefits arise from the body's shift to burning fat for energy, which can result in more efficient fat reduction and improved cognitive function.
Accurate monitoring of ketone levels is vital for individuals adhering to a ketogenic diet. Sustaining ketone levels within the ideal range guarantees effective fat burning and overall health.
However, heightened ketone levels beyond this range may indicate underlying health concerns, necessitating medical evaluation to preclude conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
When Ketones Build Up
When the body experiences insufficient insulin levels, ketones can accumulate, leading to serious health complications. This buildup occurs when the body cannot effectively utilize glucose for energy, prompting the breakdown of fats and the subsequent release of ketones into the bloodstream.
Several causes of accumulation include missed insulin injections, increased insulin needs during periods of illness, injury, surgery, pregnancy, or menstruation. Regular glucose monitoring is crucial during the initial phase of the ketogenic diet to maintain safe ketone levels and adjust as needed.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to adopt effective prevention strategies:
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor blood sugar levels, especially during periods of increased insulin requirements, to detect and address heightened ketone levels promptly.
- Consistent Insulin Management: Guarantee consistent administration of insulin as prescribed, avoiding missed doses, and adjusting insulin intake during times of physiological stress.
- Health Awareness: Maintain awareness of individual insulin needs and monitor for signs of illness or stress that may necessitate adjustments in insulin therapy.
High ketone levels can be a precursor to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a potentially life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Recognize Ketone Symptoms
Recognizing ketone symptoms is vital for those on a ketogenic diet to guarantee safety and effectiveness. A notable indicator is a fruity breath odor, which results from acetone, a byproduct of fat metabolism.
Additionally, monitoring blood sugar levels is essential, especially for individuals with diabetes, to prevent the escalation of ketone levels into diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
Blood tests are considered the gold standard for accuracy and provide real-time data, which can be particularly important for effective ketosis management.
Detecting Fruity Breath
A notable symptom of ketosis is the presence of a fruity breath odor, which arises from the production of acetone, one of the primary ketone bodies generated during fat metabolism.
This distinctive smell can serve as a useful indicator for individuals on a ketogenic diet, affirming that their bodies are effectively breaking down fat for energy. However, the odor, often termed "keto breath," can be socially noticeable and may require specific strategies to mitigate.
Understanding the mechanisms behind fruity breath can help in managing this symptom more effectively. Here are three actionable steps:
- Hydration: Increasing water intake can help dilute the concentration of ketones in the breath, reducing the intensity of the odor.
- Oral Hygiene: Enhanced dental care routines, including brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, can greatly alleviate the smell.
- Diet Adjustments: Incorporating more fibrous vegetables and adjusting protein intake may help balance ketone levels and reduce breath odor.
Implementing these fruity breath remedies and social strategies can help individuals maintain their ketogenic diet while managing any potential social discomfort.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Monitoring blood sugar levels is an important practice for individuals on a ketogenic diet, as it provides valuable insights into metabolic health and the risk of complications such as ketoacidosis. Increased blood sugar levels can indicate insufficient insulin management or imminent ketoacidosis, necessitating immediate intervention.
Recognizing symptoms of high ketone levels, such as fruity breath odor, frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, and stomach pain, is vital for timely response and prevention of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is particularly important during illness or stress, as these conditions can heighten insulin requirements. Regular checks enable timely adjustments to insulin dosages, mitigating potential hyperglycemia and subsequent ketoacidosis.
Symptoms like fruity breath odor often accompany hyperglycemia and signal an urgent need to reassess blood sugar and ketone levels.
Consulting with healthcare professionals for tailored diabetes management support is recommended. Personalized guidance guarantees proper monitoring and effective responses to abnormal ketone levels, safeguarding against the severe consequences of DKA.
Types of Ketone Testing
When starting a ketogenic diet, understanding the various methods for testing ketone levels is essential for effectively monitoring and enhancing nutritional ketosis. There are three primary types of ketone testing: blood, breath, and urine. Each method varies regarding testing frequency, accuracy comparison, and cost. Regular glucose monitoring is also important to maintain safe ketone levels.
1. Blood Testing: Blood ketone meters measure beta-hydroxybutyrate levels, providing the most accurate assessment of ketosis. The ideal range for nutritional ketosis is typically 0.5 to 3.0 mmol/L.
Blood tests are highly precise, but the cost of test strips, about $1 each, can make frequent testing expensive.
2. Breath Testing: Breath analyzers, such as Ketonix, measure acetone levels in exhaled breath. This method is non-invasive and convenient, yet may offer less accuracy compared to blood tests.
Breath testing is beneficial for those seeking a cost-effective and reusable option, though it requires careful interpretation due to variability in measurement.
3. Urine Testing: Urine test strips detect acetoacetate levels and are the most affordable option, costing around 5 cents per test.
While useful for initial testing, their reliability decreases over time as the body adapts to ketosis.
Urine Ketone Testing
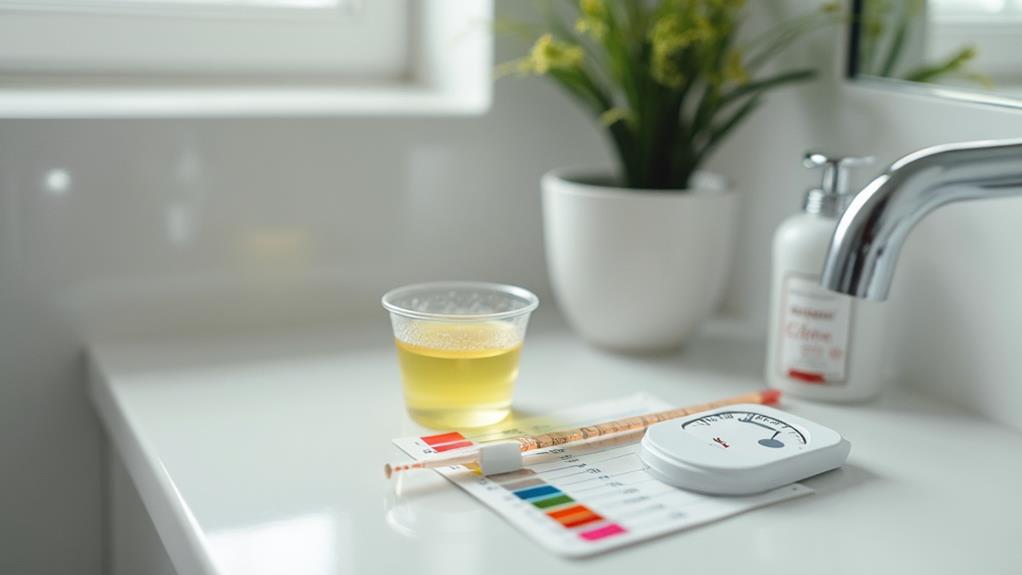

When selecting urine ketone test strips, individuals should consider brands that provide clear instructions and reliable color charts for accurate interpretation.
The testing procedure involves immersing the strip in a urine sample and comparing the resulting color change to the provided chart within the recommended timeframe.
Consistent testing at the same time each day guarantees more reliable monitoring of ketosis levels, although users should be aware of the limitations in long-term accuracy.
Choosing Test Strips
Urine ketone test strips offer an affordable and convenient method for measuring ketosis, making them an attractive option for many individuals on a ketogenic diet. Costing approximately 5 cents per test, they present a cost-effective alternative compared to more expensive blood and breath testing methods.
These strips detect acetoacetate levels in urine through a chemical reaction involving sodium nitroprusside, which results in a color change indicating the relative concentration of ketones.
When selecting urine ketone test strips, consider the following factors:
- Cost Comparison: Evaluate the price per test among different brands to guarantee affordability. While most strips are economical, prices can vary slightly.
- Accuracy Factors: Understand that the accuracy of urine test strips can decrease over time as the body becomes more efficient at utilizing ketones. They are most reliable during the initial stages of the ketogenic diet.
- Consistency: For consistent results, it is advisable to test at the same time each day. Many users prefer morning testing to establish baseline ketone levels.
While urine ketone test strips are particularly useful for beginners to gauge initial ketosis, their reliability may diminish as the body adapts.
Testing Procedure Steps
After selecting an appropriate brand of urine ketone test strips, the next logical step is to properly understand and execute the testing procedure to obtain accurate results. Start by collecting a clean urine sample in a container, guaranteeing it is free from any contaminants. This step is essential to avoid any interference with the test results.
Next, dip the urine test strip into the sample for a few seconds and then remove it, allowing any excess urine to drip off. It is important to follow the instructions on the packaging precisely to make sure the strip is exposed to the urine sample for the correct duration.
Wait for the specified time indicated on the test strip packaging, usually about 15 seconds. After this waiting period, proceed to the color comparison step. Compare the color change on the strip to the provided color chart, which will help you determine the concentration of ketones present.
To maintain the accuracy and reliability of the test strips, store them in a cool, dry place and avoid exposure to moisture or heat.
| Step | Action | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Collect Sample | Collect clean urine sample | Guarantee container is contaminant-free |
| 2. Dip Strip | Dip strip into urine sample | Allow excess urine to drip off |
| 3. Wait and Compare | Wait for 15 seconds, then compare color change | Use provided color chart |
Using these precise steps makes sure accurate monitoring of ketone levels through urine testing.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting the results of urine ketone tests requires an understanding of how the test strips measure acetoacetate, a type of ketone body. The color change on the strip corresponds with ketone concentration, where darker urine color indicates higher ketone levels, suggesting a higher likelihood of being in ketosis.
To guarantee consistency, it is recommended to maintain a regular testing frequency, ideally at the same time each day, such as in the morning after an overnight fast.
However, it is important to note that while urine ketone testing is a cost-effective method, it has limitations for long-term monitoring. Over time, the body becomes more efficient at utilizing ketones, which can result in lower acetoacetate levels in the urine despite stable blood ketone levels. Consequently, individuals on a ketogenic diet for an extended period may find urine tests less reliable.
For effective interpretation of urine ketone test results, consider the following steps:
- Monitor urine color: Darker colors indicate higher ketone levels.
- Maintain consistent testing frequency: Test at the same time each day.
- Understand limitations: Urine tests may not accurately reflect blood ketone levels in long-term ketogenic dieters.
Blood Ketone Testing
Blood Ketone Testing
Blood ketone testing is a highly precise method for measuring the level of beta-hydroxybutyrate, the primary ketone body produced during fat metabolism. Utilizing a small blood sample obtained via a finger-stick, this method offers the most accurate indication of ketosis.
To maintain ketosis, it's essential to keep carbohydrate intake within recommended limits and monitor ketone levels regularly. The ideal range for nutritional ketosis is between 0.5 and 3.0 mmol/L. Levels exceeding this range can indicate a risk of ketoacidosis, particularly for individuals with diabetes.
To guarantee accurate results, meter calibration is important. Calibrating your meter regularly ensures that the readings reflect true ketone levels. Additionally, the cost of each test strip, approximately $1, emphasizes the importance of budgeting for sufficient supplies to maintain consistent monitoring.
For those new to the keto lifestyle, frequent testing is key to understanding how your body responds to dietary changes. Regular testing frequency is recommended, especially during the initial phases of a ketogenic diet.
Frequent checks help track progress and allow for necessary dietary adjustments to maintain desired ketosis levels. It's critical to have a reliable meter and an ample supply of test strips to facilitate this regular monitoring.
Breath Ketone Testing
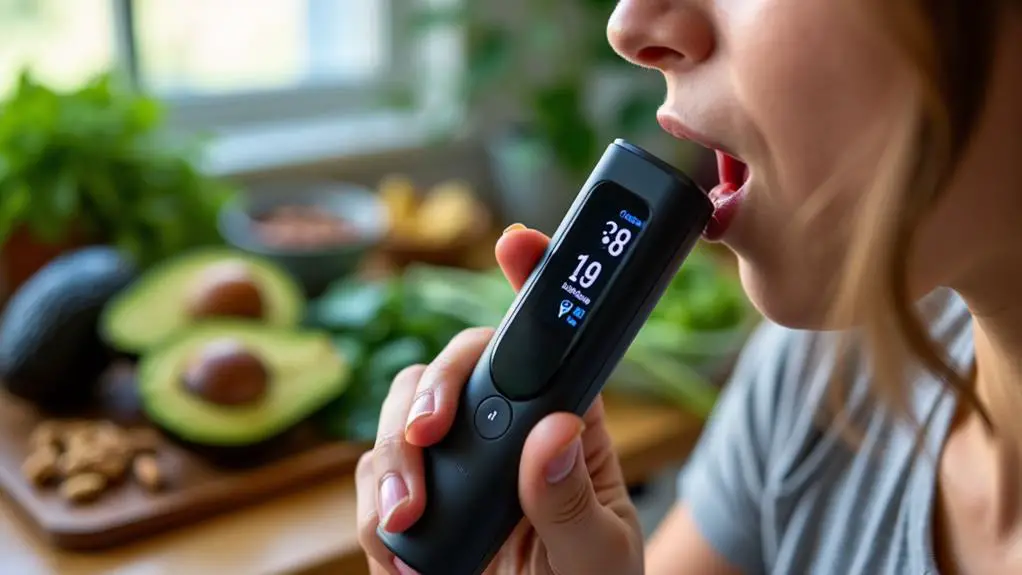

Breath ketone testing, utilizing devices such as Ketonix and Keto Stat, offers a non-invasive method to measure acetone levels, reflecting ketosis status.
These devices require minimal setup and no additional supplies, making them convenient for frequent use.
For accurate and reliable results, it is advisable to test under consistent conditions, considering factors like hydration, recent food intake, and exercise.
Breath Ketone Devices
With the rise in popularity of the ketogenic diet, breath ketone devices have emerged as a valuable tool for monitoring ketosis. These devices measure acetone levels in exhaled breath, offering a non-invasive alternative to blood tests. However, several factors influence their effectiveness.
1. Breath Device Accuracy: The precision of devices such as Ketonix and LEVL can vary, often requiring specific exhale methods and regular calibration techniques to maintain reliability.
While less accurate than blood tests, they provide a cost-effective means for frequent monitoring.
2. Impact Factors: The accuracy of breath ketone readings can be affected by external elements such as alcohol consumption and other substances present in the breath, potentially leading to interpretation challenges.
Therefore, user experiences may differ greatly based on these variables.
3. Monitoring Frequency: Regular use of breath ketone devices allows individuals to track their ketosis status and make dietary adjustments accordingly.
This can foster better adherence to a ketogenic lifestyle, despite the potential for device comparisons to reveal variability in readings.
Testing Procedure Tips**
For best results when using breath ketone testing devices, it is imperative to adhere to specific procedural guidelines.
Breath ketone testing devices, such as Ketonix and Keto Stat, measure acetone levels in exhaled breath, providing a non-invasive method to monitor ketosis. To guarantee accurate readings, proper calibration of the device according to the manufacturer's instructions is essential, along with allowing the device to warm up if specified.
Testing frequency plays a significant role in obtaining reliable data. It is recommended to test at the same time each day, ideally in a fasting state, to maintain consistency and reliability in results. This approach minimizes variables that could affect ketone levels, making sure that readings reflect true metabolic states rather than transient fluctuations.
Avoiding food and beverages immediately before testing is important, as consumption can skew breath ketone levels, leading to inaccurate measurements. Ideal conditions for testing involve a clean, dry mouth and an empty stomach.
Regular cleaning and maintenance of the breath ketone testing device are also critical to guarantee its accuracy and longevity.
Adhering to these procedural guidelines will enhance the reliability of breath ketone measurements, aiding in effective monitoring of ketosis on a keto diet.
Interpret Ketone Results
Interpreting ketone results is vital for individuals on a keto diet to understand their metabolic state and guarantee they remain within safe and effective ranges.
Recognizing ketone variations and ideal levels helps tailor the diet for desired outcomes, such as weight loss or improved metabolic health. Monitoring blood ketone levels can also provide insights into how well the body is adapting to the diet and ascertain that individuals stay within the ideal range for fat burning.
1. Nutritional Ketosis and Ideal Levels
Nutritional ketosis is achieved when blood ketone levels range between 0.5 to 3.0 mmol/L. For optimal weight loss, a range of 1.5 to 3.0 mmol/L is considered ideal, indicating enhanced fat metabolism.
Levels above 3.0 mmol/L, however, may suggest a risk of ketoacidosis, particularly in individuals with diabetes.
2. Testing Methods and Accuracy
Blood ketone meters measure beta-hydroxybutyrate, providing the most accurate assessment of ketosis.
Urine test strips, which track acetoacetate, can show variable results due to adaptation, potentially leading to lower readings over time.
Breath tests measure acetone and, while less precise, offer a cost-effective and convenient testing alternative.
3. Testing Frequency
Regular testing frequency is important for monitoring ketone levels and adjusting the diet accordingly.
Consistent tracking helps identify ketone variations, guaranteeing individuals stay within their target range and make informed dietary adjustments for ideal results.
Manage High Ketone Levels

Monitoring ketone levels is fundamental for maintaining a safe and effective keto diet. Increased ketone levels, particularly above 3.0 mmol/L, can signal a risk of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in individuals with diabetes, necessitating immediate attention and intervention.
Symptoms such as fruity breath, excessive thirst, frequent urination, and increased fatigue indicate high ketone levels and require prompt ketone management to prevent complications. Staying hydrated is essential, as dehydration can exacerbate these symptoms and increase the risk of kidney stones.
Regular blood sugar monitoring is vital, especially during periods of illness, stress, or changes in routine, as these factors can increase insulin requirements and boost ketone levels. Should high ketone levels be detected, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider or diabetes management team to obtain proper guidance and avoid potential health risks.
Utilizing ketone testing methods, such as blood or urine tests, is effective for tracking ketone levels and ensuring timely responses to significant increases.
Dietary adjustments may also be necessary to manage high ketone levels. Reducing carbohydrate intake gradually, ensuring adequate hydration, and balancing macronutrients can aid in stabilizing ketone production and maintaining overall metabolic health.
Monitor Ketone Trends
Regularly tracking ketone trends is an essential aspect of enhancing your ketogenic diet, providing valuable insights into your metabolic state and fat utilization efficiency. By measuring ketone levels consistently, particularly within the ideal range of 0.5 to 3.0 mmol/L, you can better understand how effectively your body is utilizing fat for fuel.
Staying hydrated and replenishing electrolytes can also impact ketone levels, helping to alleviate discomfort and guarantee accurate readings. Establishing a routine of consistent testing at the same time each day helps to create a reliable baseline, allowing you to identify and analyze ketone fluctuations.
To monitor ketone trends effectively, consider the following strategies:
- Consistent Timing: Test your ketone levels at the same time each day to minimize variability and establish a clear baseline.
- Log Data: Maintain a detailed log of your ketone measurements, dietary intake, physical activity, and stress levels. This helps in tracking patterns and understanding what factors influence your ketosis state.
- Weekly Checks: Once nutritional ketosis is achieved, aim for weekly checks to monitor trends. This reduces the need for daily testing and helps maintain motivation by tracking long-term progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should You Check Ketones on a Keto Diet?
To determine ketone levels on a keto diet, initial daily checks are recommended for confirming nutritional ketosis. Subsequently, weekly testing is usually adequate. Best testing methods include morning tests and post-meal assessments for ideal timing and accuracy.
What Is the Easiest Way to Monitor Ketone Levels?
The easiest way to monitor ketone levels is using urine strips for a quick and cost-effective method, though blood ketone meters provide more accurate results, ideal for precise long-term monitoring despite their higher expense and invasiveness.
What Is the Ideal Ketone Level for Ketosis?
The ideal ketone level for ketosis ranges between 1.5 to 3.0 mmol/L, maximizing fat utilization for energy. Various ketone measurement methods, such as blood, urine, and breath tests, can help monitor these optimal ketone levels effectively.
How Do I Know if I'm in Ketosis on the Keto Diet?
To determine if you are in ketosis, monitor symptom recognition such as fruity breath, increased thirst, and reduced appetite. Utilize blood ketone meters for accurate measurement and make dietary adjustments to maintain ideal ketone levels.
Conclusion
Monitoring ketone levels is vital for individuals following a ketogenic diet. Understanding the nature of ketones, recognizing symptoms of ketone build-up, and utilizing various testing methods, such as urine and breath tests, can provide essential insights. Proper interpretation of ketone results, along with effective management of raised levels, guarantees ideal dietary outcomes. Continual monitoring of ketone trends facilitates informed adjustments, promoting metabolic health and adherence to the ketogenic regimen.








No Comments