
The keto diet supports weight loss by flipping your body's energy switch from carbs to fats, making you a fat-burning machine! When you eat fewer carbs, your body enters ketosis, burning fat for fuel instead. This process also stabilizes blood sugar and insulin levels, making you less hungry and reducing cravings. Plus, the high fat and protein in your meals keep you full longer, so you eat less. It sounds pretty cool, right? By sticking to the keto plan, users can maintain steady energy and preserve muscle mass while losing weight. Curious about more details? Keep digging!
Key Takeaways
- The ketogenic diet induces ketosis, where the body burns fat for energy instead of glucose, enhancing fat oxidation.
- Reduced carbohydrate intake lowers insulin levels, aiding fat burning and improving glycemic control.
- High-fat and protein foods promote prolonged satiety, reducing hunger and controlling cravings.
- Ketone production and regular monitoring help optimize fat burning and maintain ketosis.
- The ketogenic diet preserves muscle mass during weight loss by supporting muscle repair and growth with high protein intake.
What Is the Keto Diet?
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate dietary regimen designed to shift the body's primary energy source from glucose to fat. It was first introduced in the 1920s to help manage epilepsy.
Imagine treating seizures with food instead of medicine! Fast forward to the 1970s, the keto diet grabbed the spotlight again, this time for weight loss, thanks to the Atkins diet.
So, what are the basic dietary guidelines? Think of your plate: 70-75% of it should be fats like avocados, oils, and fatty meats. Protein takes up 20-25%, so think chicken, fish, or eggs.
Carbohydrates? Just 5-10%, which means saying goodbye to bread, pasta, and sugary treats. The goal? To push your body into a state called ketosis where it burns fat instead of glucose for energy. Sounds magical, right?
Foods you'll be munching on include low-carb veggies like spinach and broccoli, and some dairy products like cheese. But grains, sugars, and starchy foods are out.
Studies show keto can help you lose weight and lower blood sugar and triglyceride levels. It's like a win-win for your waistline and your health!
Ketosis and Energy Metabolism
When you eat fewer carbs on a keto diet, your body starts using fat for energy, not sugar.
This process happens in the liver, where fats get turned into something called ketone bodies, which even your brain can use for fuel.
As you burn more fat and keep your blood ketone levels just right, you might notice you feel less hungry and start losing weight more easily.
Ketone Production Process
Often considered a cornerstone of the ketogenic diet, ketosis is a metabolic state that arises from considerably reducing carbohydrate intake. In this state, the body undergoes a fascinating process known as ketone synthesis, where it shifts from using glucose to burning fat for energy. This metabolic adaptation is fundamental for anyone following a keto diet.
When carbohydrate intake plummets to less than 50 grams per day, the body's insulin levels drop dramatically. This decrease in insulin allows fatty acids to be released from fat stores in adipose tissue.
These fatty acids travel to the liver, where they are converted into ketones. These ketones then serve as an essential energy source for various tissues, including the brain, which would otherwise rely on glucose.
To guarantee you're effectively in ketosis, monitoring blood ketone levels is critical. This helps confirm that your body is utilizing fat for energy instead of glucose.
- Key points to remember:
- Ketosis starts with a major reduction in carbs
- Insulin levels drop considerably
- Fatty acids are released and converted into ketones
- The brain and other tissues use ketones for energy
- Monitoring ketone levels confirms effective ketosis
Understanding this process highlights why the keto diet can be so effective for weight loss and metabolic health.
Fat Utilization Mechanism
Upon entering ketosis, the body undergoes a dramatic shift in its energy metabolism, prioritizing fat as its primary fuel source. This shift enhances fat oxidation, allowing the body to break down stored fat into fatty acids and glycerol. These fatty acids are then converted into ketone bodies, which serve as an alternative energy source, especially for the brain. Remarkably, ketone bodies can supply up to 70% of the brain's energy needs during ketosis, making the process highly energy efficient.
As insulin levels drop due to low carbohydrate intake, the body promotes lipolysis, further enhancing fat utilization. This metabolic state is sustained by the typical macronutrient ratio of the ketogenic diet:
| Macronutrient | Percentage of Diet | Role in Ketosis |
|---|---|---|
| Fats | 70-80% | Primary fuel source, enhances fat oxidation |
| Proteins | 10-20% | Maintains muscle mass |
| Carbohydrates | 5-10% | Minimal to trigger ketosis |
Research shows that those on a ketogenic diet often experience greater weight loss and improved metabolic markers, such as decreased triglycerides and increased HDL cholesterol, compared to traditional low-fat diets. This makes the ketogenic diet an effective strategy for weight loss and energy efficiency.
Insulin and Blood Sugar Levels
Insulin regulation stands as a cornerstone in the efficacy of the ketogenic diet, particularly in its impact on blood sugar levels. By markedly lowering carbohydrate intake, the ketogenic diet enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes blood sugar stabilization. This means your body doesn't need to produce as much insulin, which helps to reduce fat storage and increase fat burning for energy.
When you enter a state of ketosis, the body shifts its energy reliance to ketone bodies produced from fat breakdown. This not only fuels the body but also stabilizes blood sugar levels. Research has shown that individuals on a ketogenic diet experience improved glycemic control, with studies indicating a reduction in HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetes patients by up to 20%.
Lower insulin levels are essential for regulating appetite, as stable insulin levels prevent the fluctuations that often lead to cravings and overeating. The average blood glucose levels in participants following a ketogenic diet have shown notable reductions, with initial levels of 7.26 mmol/L decreasing to 5.62 mmol/L after 24 weeks.
- Enhances insulin sensitivity
- Promotes blood sugar stabilization
- Reduces fat storage
- Increases fat burning
- Improves glycemic control
Appetite Regulation
Stabilizing insulin levels through a ketogenic diet plays a pivotal role in appetite regulation, primarily by reducing hunger and controlling cravings. When your body consumes fewer carbs, insulin levels stabilize, which helps keep hunger signals in check. This hormonal balance is key because it makes you less likely to crave high-carb snacks that can derail your diet.
Another neat thing about keto is that high-fat and protein foods take longer to digest than carbs. This means you feel full for a longer time, potentially eating less throughout the day. Imagine not constantly thinking about your next meal – sounds pretty good, right?
Research even shows that people on a keto diet have lower levels of ghrelin, the hormone that tells you when you're hungry. With less of this hormone floating around, you're less likely to experience those annoying hunger pangs.
But here's the catch: you have to stick to the diet strictly, with no cheat days, to keep the benefits rolling. Consistency is essential for maintaining ketosis and enjoying its appetite-regulating perks.
Fat Burning Mechanism
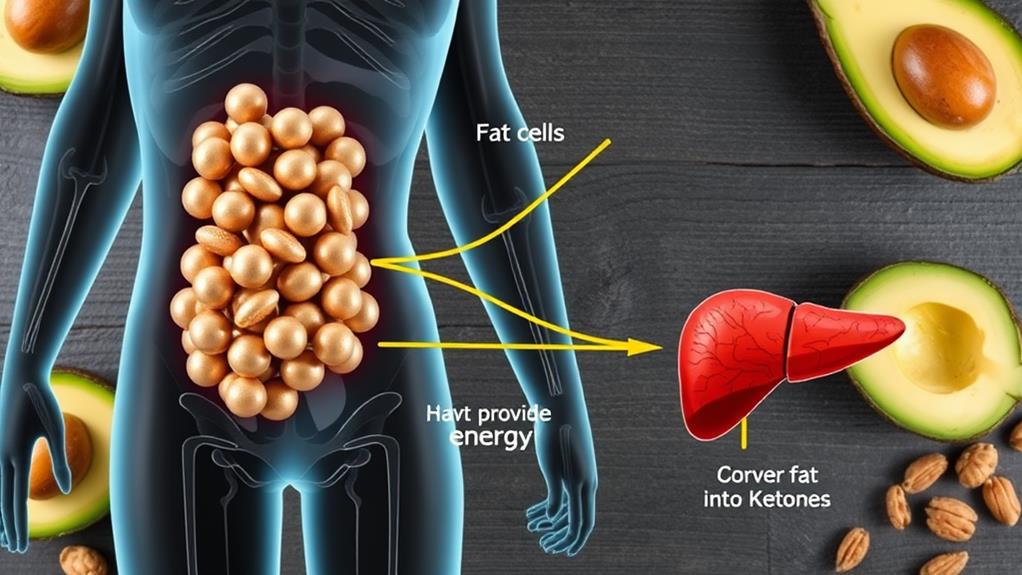
The ketogenic diet's fat-burning magic kicks in when you cut down on carbs, pushing your body into ketosis.
This is a state where your liver transforms fatty acids into ketone bodies, which your brain and organs can use for energy instead of glucose.
Ketosis and Energy Source
When the body enters a state of ketosis, it undergoes a significant metabolic shift where fats become the primary energy source instead of carbohydrates. This change in energy dynamics is one of the notable ketosis benefits that drive effective weight loss.
In ketosis, the liver plays an essential role by converting fatty acids into ketone bodies. These ketones then serve as an alternative energy source for the brain and other critical organs, enhancing fat burning.
Studies indicate that after just 3-4 days of carbohydrate restriction, the body begins to rely mainly on its fat stores. This metabolic adjustment results in effective weight loss and fat reduction.
In addition, the reduction in insulin levels associated with the ketogenic diet facilitates lipolysis. Lipolysis is the process by which stored fat is broken down and used for energy, further promoting fat burning.
To guarantee the body remains in this fat-burning mode, regular monitoring of blood ketone levels is essential. This confirms the state of ketosis and supports ongoing weight loss efforts.
- Metabolic shift: Fats become the primary energy source.
- Liver function: Converts fatty acids into ketones.
- Carb restriction: Prompts reliance on fat stores.
- Insulin reduction: Facilitates lipolysis.
- Monitoring: Confirms ketosis state.
Thus, the ketogenic diet's fat-burning mechanism is both intricate and effective.
Insulin and Appetite Regulation
A key factor in the ketogenic diet's effectiveness for weight loss is its profound impact on insulin levels and appetite regulation. When you eat fewer carbs, your body makes less insulin. This is super important because insulin helps control blood sugar levels and affects hunger hormones. Lower insulin means your blood sugar stays stable, and you don't get those crazy hunger pangs that make you want to eat everything in sight.
But wait, there's more! When you're in ketosis, your body burns fat for energy instead of sugar. This produces ketone bodies, which not only fuel you but also make you feel less hungry. So, you're burning fat and not feeling as hungry—how cool is that?
Eating lots of fats and proteins, like you do on a keto diet, also helps. These foods take longer to digest, keeping you full for longer periods. No more mid-day snack attacks!
Studies show that stable insulin levels prevent the ups and downs that lead to cravings and overeating. Plus, the keto diet improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of insulin resistance, which is linked to weight gain.
This all adds up to better appetite control and more effective weight loss.
Monitoring Ketone Levels
Understanding insulin's role and its regulation in the ketogenic diet naturally leads to the importance of monitoring ketone levels to guarantee effective fat burning. When you're on a keto diet, keeping an eye on your ketone levels is key to knowing if you're truly in ketosis and burning fat instead of carbs.
You see, ketone bodies like beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone are produced in your liver when you eat very few carbs. These act as a super fuel for your brain and body.
Using different ketone testing methods can help you keep track of your progress. Here are some methods you can use:
- Blood ketone meters: These are super accurate.
- Urine test strips: Easy to use, but not always precise.
- Breath analyzers: Convenient, but can be pricey.
- Regular monitoring: Helps tweak your diet for best results.
- Ketone levels: Aim for 0.5 to 3.0 mmol/L for top fat burning.
Regularly checking your ketones means you can adjust your fat and carb intake to stay in that sweet spot for fat burning. If your levels are above 1.5 mmol/L, you're likely burning fat like a pro.
Keep testing, and keep burning!
Impact on Muscle Mass
Numerous studies have highlighted the ketogenic diet's unique ability to preserve muscle mass during weight loss, setting it apart from other low-calorie diets. This muscle preservation is vital because it helps maintain strength and function while shedding fat.
The keto diet encourages the body to use fat for energy, which means less muscle protein breakdown and more muscle left intact. One key to this process is protein synthesis. On a ketogenic diet, protein makes up about 20-25% of what you eat. This high protein intake is essential for repairing and growing muscles.
Lower insulin levels on keto also mean muscles are more likely to be preserved, as insulin can sometimes promote muscle breakdown. Research backs this up. People on a keto diet lose weight—about 13% of their body weight over eight weeks—without losing muscle like those on higher-carb diets might.
Plus, being in nutritional ketosis helps muscles recover and perform better, especially during resistance training.
Short-Term Weight Loss

While the ketogenic diet's impact on muscle mass preservation is remarkable, its potential for short-term weight loss is equally significant.
Studies show that participants can lose up to 13% of their body weight within just eight weeks on a low-carb, high-fat regimen. This rapid weight loss is primarily due to the body shifting to burning fat for energy, which also leads to a substantial drop in water weight as glycogen stores are depleted.
One of the best things about the keto diet is that it can help curb your appetite. Lower ghrelin levels, the hormone that makes you hungry, mean you might not feel as hungry as usual.
Plus, improved insulin sensitivity plays a role, especially for those with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. Effective meal planning and choosing the right snack options can further enhance these benefits.
- Rapid initial weight loss: Lose up to 13% of body weight in eight weeks.
- Enhanced fat burning: Switches body to fat as the primary energy source.
- Appetite control: Reduced hunger hormone levels make you feel less hungry.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Beneficial for those with insulin resistance.
- Effective meal planning: Key to maximizing short-term weight loss results.
Long-Term Health Effects
Over extended periods, the ketogenic diet has demonstrated significant impacts on body weight and metabolic health. Long-term benefits include substantial reductions in body weight and BMI. For instance, obese patients saw their weight drop from an average of 101.03 kg to 86.67 kg over 24 weeks. This is a huge deal if you've ever tried to lose even a little weight!
Another great thing about keto is its positive effect on cardiovascular health. Triglycerides, which are fats in your blood that can raise the risk of heart disease, plummeted from 2.75 mmol/L to 1.09 mmol/L. Plus, HDL cholesterol, the good kind, improved. So, it's not just about looking better; it's about feeling better on the inside too.
But, it's not all sunshine and rainbows. There are some health implications to take into account. Risks like nutrient deficiencies, kidney stones, and raised uric acid levels mean you need to be careful. This isn't a diet to jump into without some planning.
Long-term studies show that while keto is great for weight loss and metabolic health, we need more research to fully understand its long-term effects, especially on kidneys and liver.
Research and Studies
Building on the long-term health effects, the body of research and studies on the ketogenic diet provides robust evidence supporting its efficacy in weight loss and metabolic improvements. This isn't just some fad; science backs it up with real numbers and results.
For instance, a meta-analysis of 13 studies found that people on a ketogenic diet lost more weight and had lower triglyceride levels than those on low-fat diets after one year.
That's not all. When it comes to reducing hunger, the keto diet shines. One study showed participants lost 13% of their weight and had decreased ghrelin levels over 8 weeks.
Another study lasting 24 weeks on obese patients reported impressive results: an average weight drop from 101.03 kg to 86.67 kg and a significant BMI reduction.
Additionally, the ketogenic diet improves metabolic markers, like lowering blood glucose from 7.26 mmol/L to 5.62 mmol/L. Long-term adherence also benefits lipid profiles, reducing total cholesterol and LDL while increasing HDL cholesterol.
- Greater weight loss compared to low-fat diets
- Significant decrease in hunger and appetite
- Average weight reduction over 24 weeks
- Improved blood glucose levels
- Better lipid profiles with long-term adherence
These findings highlight how effective nutritional strategies and metabolic adaptations can be with the ketogenic diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Keto Help You Burn Fat?
Yes, keto benefits fat metabolism by markedly reducing carbohydrate intake, thereby inducing ketosis. This metabolic state enhances fat oxidation and mobilization, leading to efficient utilization of stored fat for energy and promoting substantial weight loss.
How Does the Keto Diet Work Scientifically?
The keto diet works scientifically by inducing the ketosis process, where metabolic changes shift the body from using glucose to burning fat for fuel. This shift reduces insulin levels, enhances lipolysis, and increases the production of ketone bodies.
How Does Fat Leave the Body on Keto?
On a ketogenic diet, fat metabolism involves the breakdown of triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids, which are then converted to ketones. These ketone bodies are utilized for energy, facilitating fat loss through sustained ketone production.
How Does Keto Work With so Much Fat?
The ketogenic diet, despite common keto misconceptions, promotes fat adaptation by shifting the body's energy source from carbohydrates to fats. This process enables efficient fat metabolism, leading to significant weight loss while maintaining energy levels.
Conclusion
The keto diet promotes weight loss by inducing ketosis, a metabolic state where the body uses fat for energy instead of carbs. This process regulates insulin and blood sugar levels, reduces appetite, and enhances fat burning while preserving muscle mass. Research indicates notable short-term weight loss benefits, although long-term health effects require further study. Understanding the science behind keto provides valuable insights for those considering this dietary approach for weight management.









No Comments